The most important consequence of the war in Ukraine is the lives lost and the humanitarian crisis associated with the huge numbers of besieged and displaced people. There are also, however, numerous significant economic implications.
Prior to the outbreak of the war, most key global macroeconomic variables were seen as returning to normality over 2022-23 following the COVID-19 pandemic.
Global growth in 2023 was projected to return to rates similar to those prevailing in the immediate pre-pandemic period.
Most OECD economies were expected to get back to full employment by 2023, and inflation was seen as converging on levels close to policy objectives, though later and from higher levels than previously expected in most countries.
Policy settings were also expected to normalise, with exceptional monetary policy accommodation being progressively removed and emergency fiscal measures, taken in response to the pandemic, phased out.
Although Russia and Ukraine are relatively small in output terms, they are large producers and exporters of key food items, minerals and energy. The war has already resulted in sizeable economic and financial shocks, particularly in commodity markets, with the prices of oil, gas and wheat soaring.
The moves in commodity prices and financial markets seen since the outbreak of the war could, if sustained, reduce global GDP growth by over 1 percentage point in the first year, with a deep recession in Russia, and push up global consumer price inflation by approximately 2½ percentage points.
Well-designed and carefully targeted fiscal support could reduce the negative impact on growth with only a minor extra impetus to inflation. In some countries, this could be funded by taxation of windfall gains.
Faced with a new negative shock of uncertain duration and magnitude, monetary policy should remain focused on ensuring well-anchored inflation expectations. Most central banks should continue their pre-war plans, with the exception of the most affected economies, where a pause may be needed to fully assess the consequences of the crisis.
In the near term, many governments will need to cushion the blow of higher energy prices, diversify energy sources and increase efficiency wherever possible. For food, higher production in OECD countries, refraining from protectionism and multilateral support for logistics will help the countries most affected by a disruption to supply from Russia and Ukraine.
The war has underlined the importance of minimising dependence on Russia for key energy imports. Policymakers should reconsider the appropriateness of market design with a view to ensuring energy security and putting incentives in place to ensure the green transition in a publicly supported way.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine is a major humanitarian crisis affecting millions of people and a severe economic shock of uncertain duration and magnitude. This note provides a first assessment of the potential impact of the conflict on the global economy, based on the shocks seen so far, and the policy implications.
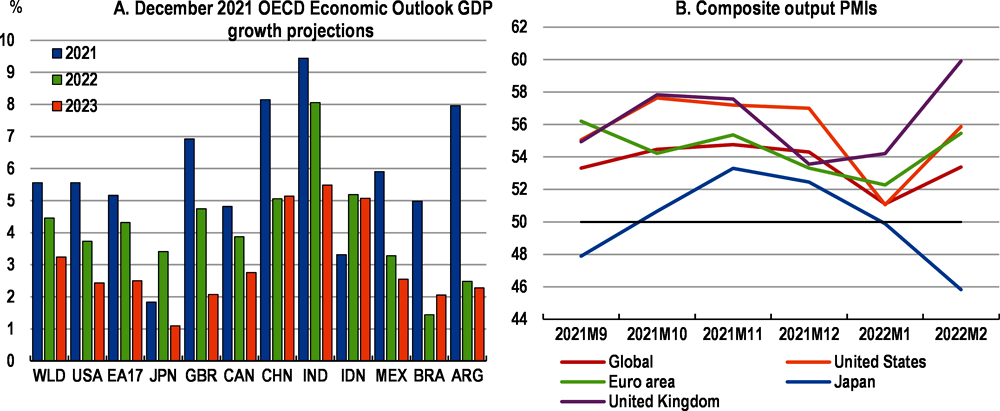
Prior to the conflict, the global recovery from the pandemic was expected to continue in 2022 and 2023, helped by continued progress with global vaccination efforts, supportive macroeconomic policies in the major economies and favourable financial conditions. The December 2021 OECD Economic Outlook projected global GDP growth of 4.5% in 2022 and 3.2% in 2023 (Figure 1, Panel A). Subsequent national accounts data and high-frequency indicators in early 2022 remained broadly consistent with this outlook, with business activity bouncing back quickly after the disruption from the Omicron variant in most countries (Figure 1, Panel B). At the same time, higher food and energy prices, supply constraints associated with the pandemic and a rapid recovery in demand from mid-2020 resulted in an acceleration and broadening of inflation in most OECD economies, especially in the United States, Latin America and many Central and Eastern European economies.
The war will hinder global growth and aggravate inflationary pressures
The war in Ukraine has created a new negative supply shock for the world economy, just when some of the supply-chain challenges seen since the beginning of the pandemic appeared to be starting to fade. The effects of the war will operate through many different channels, and are likely to evolve if the conflict deepens further.
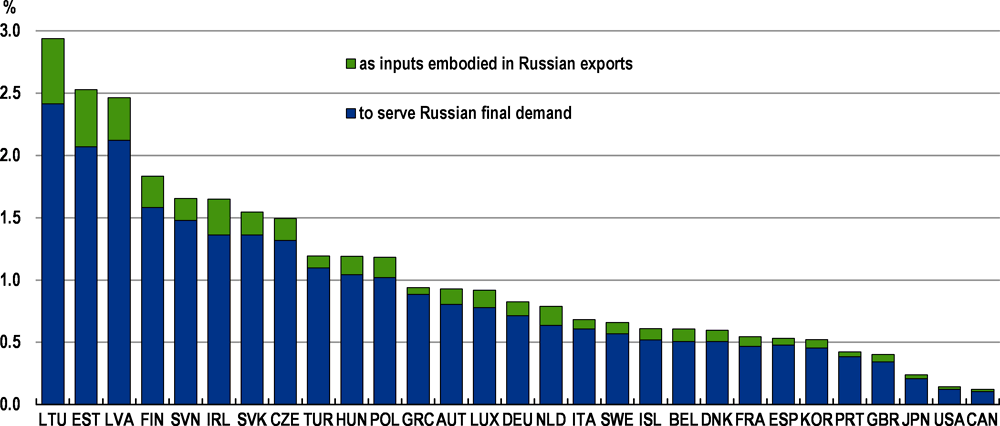
In some respects, the direct role of Russia and Ukraine in the global economy is small. Together, they account for only about 2% of global GDP at market prices and a similar proportion of total global trade, with limited bilateral trade for most countries (Figure 2). Financial linkages with other countries are also generally modest. Stocks of foreign direct investment in Russia, and by Russia in other economies, account for between 1-1½ per cent of the global total. Consolidated cross-border bank claims by BIS reporting banks on residents of Russia and Ukraine represented less than 0.5% of the global total as of the third quarter of 2021.
In one respect, however, Russia and Ukraine do have an important influence on the global economy. This is via their role as major suppliers in a number of commodity markets. Russia and Ukraine together account for about 30% of global exports of wheat, 20% for corn, mineral fertilisers and natural gas, and 11% for oil. In addition, supply chains around the world are dependent on exports of metals from Russia and Ukraine. Russia is a key supplier of palladium, used in catalytic converters for cars, and nickel, used in steel production and the manufacture of batteries. Russia and Ukraine are also sources of inert gases such as argon and neon, used in the production of semiconductors, and large producers of titanium sponge, used in aircraft. Both countries also have globally important reserves of uranium. The prices of many of these commodities have increased sharply since the onset of the war, even in the absence of any significant disruption of production or export volumes (Figure 3).
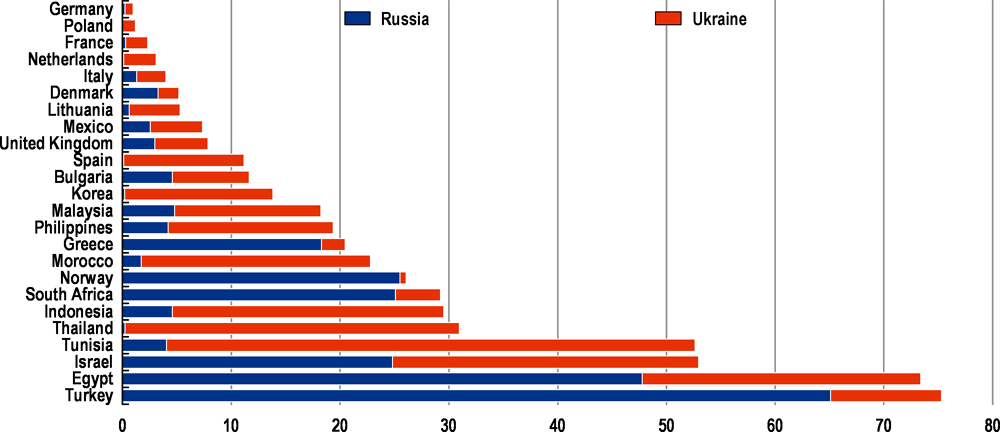
A complete cessation of wheat exports from Russia and Ukraine would result in serious shortages in many emerging-market and developing economies. There would be an acute risk not only of economic crises in some countries but also humanitarian disasters, with a sharp increase in poverty and hunger. The disruption in fertiliser manufacturing risks making these disruptions more long lasting, by putting next years’ agricultural supply under stress. In many economies in the Middle East, wheat imports from Russia and Ukraine represent around 75% of total wheat imports (Figure 4).
Despite the small economic size of Russia, the war and related sanctions are already causing disruptions of a global nature through financial and business linkages. Financial sanctions placed on Russia have targeted selected individuals and banks, reduced access to foreign capital and frozen access to the foreign exchange reserves held by the Central Bank of Russia (CBR) in the Western economies. As a result, the rouble has depreciated sharply, the CBR’s policy interest rate has risen by 10.5 percentage points to 20%, and risk premia on Russian sovereign debt have soared. Delays and difficulties in making international payments are disrupting trade and could result in debt defaults in Russia. Conditions have also tightened in financial markets around the world, reflecting greater risk aversion and uncertainty, with higher risk premia and currency depreciations also occurring in many emerging-market economies and Central and Eastern European economies with relatively strong business ties with Russia. Commercial air travel and freight are also being rerouted or ceasing operations altogether, increasing the costs of doing business, and many multinational companies have suspended operations in Russia.
There are also some possible longer-term consequences from the war, including pressures for higher spending on defence, the structure of energy markets, potential fragmentation of payment systems and changes in the currency composition of foreign exchange reserves. A re-division of the world into blocs separated by barriers would sacrifice some of the gains from specialisation, economies of scale and the diffusion of information and know-how. The exclusion from the SWIFT message system could accelerate efforts to develop alternatives. This would diminish the efficiency gains from having a single global system, and potentially reduce the dominant role of the US dollar in financial markets and cross-border payments.
Model simulations suggest a sizeable hit to global growth and higher prices if the conflict persists
The magnitude of the economic impact of the conflict is highly uncertain, and will depend in part on the duration of the war and the policy responses, but it is clear that the war will result in a substantial near-term drag on global growth and significantly stronger inflationary pressures.
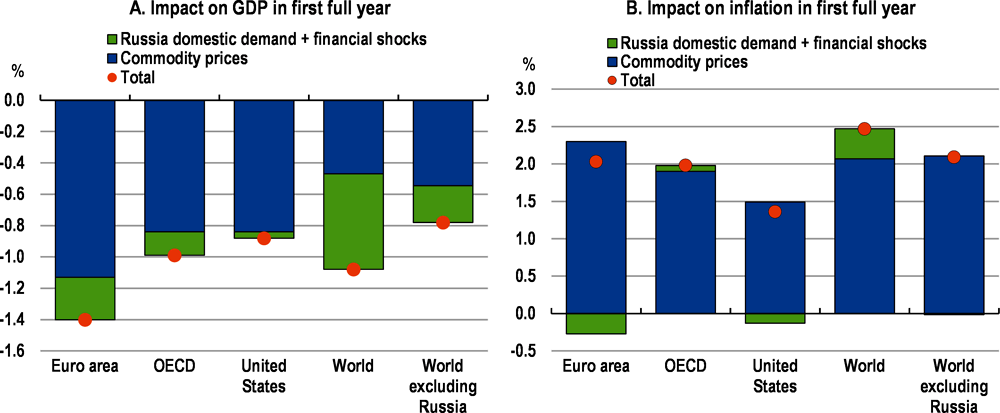
Illustrative simulations suggest that global growth could be reduced by over 1 percentage point, and global inflation raised by close to 2½ percentage points in the first full year after the start of the conflict (Figure 5). These estimates are based on the assumption that the commodity and financial market shocks seen in the first two weeks of the conflict persist for at least one year, and include a deep recession in Russia, with output declining by over 10% and inflation rising by close to 15 percentage points. (The full set of factors considered are set out in the Technical Appendix.)
The impact of the shocks differs across regions, with the European economies collectively being the hardest hit, particularly those that have a common border with either Russia or Ukraine. This reflects greater gas price rises in Europe than in other parts of the world and the relative strength of business and energy linkages with Russia prior to the conflict.
Advanced economies in the Asia-Pacific region and the Americas have weaker trade and investment links with Russia, and some are commodity producers, but growth is still hit by weaker global demand and the impact of higher prices on household incomes and spending.
Growth outcomes in the emerging-market economies reflect a balance between stronger output in some commodity-producing economies and deeper declines in the major commodity-importing economies, and the adverse impact of higher investment risk premia. Higher food and energy prices also push up inflation more than in the advanced economies.
Monetary policy reacts to the upturn in inflation around the world, with policy interest rates raised by a little over 1 percentage point on average in the major advanced economies and 1½ percentage point in the major emerging-market economies.
These simulations provide an initial look at the potential impact of the conflict based on the market dislocations observed in the first two weeks of the war. They do not incorporate many factors that could intensify the adverse effects of the conflict, such as further sanctions or consumer and business boycotts, disruptions to shipping and air traffic, the unavailability of key products from Russia, trade restrictions such as export bans on food commodities, or undermined consumer confidence.
A key potential economic risk is that energy exports from Russia to the EU could cease completely. The impact of such a shock is difficult to quantify, but could be abrupt given limited possibilities to substitute to supplies from world markets in the short term and low levels of gas reserves. One illustration of the possible additional pressures is provided by the one-day peak in European gas prices since the start of the conflict. Prices that day were 170% higher than in January, twice the size of the gas price shock assumed in the simulations above. A persistent return to prices at this level would add an additional 1¼ percentage point to inflation in Europe (taking the full shock on euro area inflation to over 3½ percentage points) and further reduce European growth by over ½ percentage point.
Input-output tables can also be used to assess the direct effects on output of a reduction in energy inputs. An illustrative decline of 20% in imported energy inputs (from direct and indirect imports of fossil fuels, refined fuel products and electricity and gas supply) would reduce gross output in the European economies by over 1 percentage point, with significant differences across countries (Figure 6). The hardest hit would be the domestic energy-producing sectors, air transport, chemicals and metals manufacturing. These estimates may understate the disruptions from lower energy availability as there could be discontinuities in the impact on output, rather than the smooth adjustment implicitly assumed in the calculations. However, it is also possible that some reduction in imported energy could be offset by stronger domestic production, drawing on reserves or improved energy efficiency.
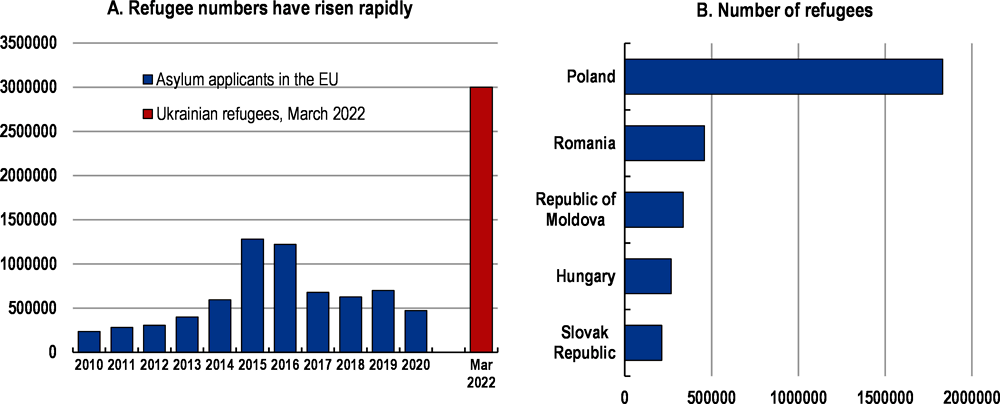
The fastest refugee flow in Europe since the end of the Second World War is underway
The humanitarian cost of the war is high and growing. Around three million people have already fled Ukraine in the first three weeks of the war (Figure 7) and that number is likely to increase further. This is considerably more than the annual flow of asylum-seekers into European countries at the height of the Syrian refugee crisis in 2015-16. Looking after the refugees from Ukraine will require spending on social and housing assistance, food provision, medical assistance and childcare and schooling.
The spending challenge is difficult to predict due to uncertainty about the number of refugees, the length of time they will stay, and the amount of spending per refugee. The cost for processing and accommodating asylum seekers for the first year in 2015-16 was estimated to be around EUR 10 000 per application by the OECD, and up to EUR 12 500 per refugee in national studies for Germany –though to varying extent across countries, depending on the level of support. At this level, the inflow of 3 million refugees seen so far could result in a direct first year cost of at least 0.25% of EU GDP, and much more in the major host economies. So far, refugees have primarily gone to a small number of countries, with Hungary, Moldova, Poland, Romania and Slovakia taking in large shares. The initial costs are manageable for the EU as a whole, but difficult to support – and deliver – by individual neighbouring countries. Burden sharing and EU support to the major host countries would allow support to be delivered more effectively.
The substantial economic costs of the conflict and elevated uncertainty add to the challenges already facing policymakers from rising inflationary pressures and the imbalanced recovery from the pandemic. Faced with an adverse supply shock of uncertain duration and magnitude from higher commodity prices, monetary policy should remain focused on ensuring well-anchored inflation expectations and intervention if needed to ensure the smooth functioning of financial markets. Additional temporary, timely and well-targeted fiscal measures, where feasible, provide the best policy option to cushion the immediate impact of the crisis on consumers and businesses, especially with rising inflation limiting the room for monetary policy manoeuvre. Regulatory measures, to improve market design in order to enhance energy security and competitiveness, can also help reduce the vulnerability to some of the energy market disruptions in the short-term and beyond.
Monetary policy should ensure well-anchored inflation expectations and stable financial market conditions
Steps towards the normalisation of monetary policy should continue in the advanced economies, albeit at a differentiated pace and with frequent reassessment as the conflict evolves. The case for continued normalisation is particularly strong in economies such as the United States, where the recovery from the pandemic is well advanced and signs of durable inflation pressures were already apparent ahead of the recent commodity price surge. A slower pace of policy normalisation is appropriate in economies where underlying (non-food non-energy) inflation remains low, wage pressures are still modest, and the adverse impact of the conflict on growth is greatest. In all countries, renewed asset purchases, expanded currency swap lines and a temporary easing of bank prudential regulations can be used if necessary to reduce tensions and liquidity shortages in financial markets.
The monetary policy stance has already been tightened substantially in some major emerging-market economies over the past year, amidst rising inflationary pressures. Higher food and energy prices are likely to require additional policy rate increases, given the greater weight of commodities in consumer price inflation. This would help to ensure stability and mitigate against potential adverse spillovers from financial market risks and monetary policy normalisation in the major advanced economies.
The conflict is creating additional fiscal pressures
Ahead of the conflict, the fiscal stance was set to tighten gradually in most advanced economies in 2022 and 2023 due to the gradual withdrawal of pandemic-related support measures and some discretionary fiscal consolidation. These plans are already being reconsidered in many countries due to the impact of the conflict. Debt service burdens remain moderate, despite sizeable fiscal deficits and higher debt levels, providing room for additional temporary and well-targeted fiscal support where needed, particularly while interest rates remain low. Immediate spending priorities include the costs of supporting refugees in Europe, and cushioning the immediate effects of the commodity and food price shocks on households and companies through temporary and well-targeted policies (see below). In the medium term, greater investment in clean energy and higher defence spending are both likely to be high on the agenda.
The scope for additional fiscal support varies considerably among emerging-market economies and developing countries, with many facing difficult trade-offs between supporting incomes and ensuring debt sustainability and investor confidence. Higher commodity prices should, however, bolster fiscal revenues in commodity-exporting countries, providing some leeway to cushion the shock of higher food and energy prices on household incomes.
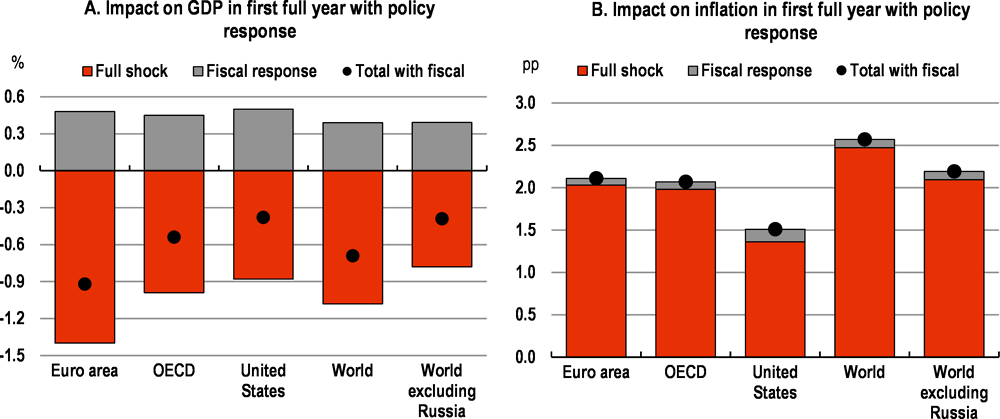
Illustrative simulations of a well-targeted rise in final government spending of 0.5% of GDP for one year in all the OECD economies show that this could offset around one-half of the estimated decline in output from the conflict without adding significantly to inflation (Figure 8). Non-OECD economies would also benefit, albeit to a lesser extent, even if they do not have sufficient fiscal space to undertake additional fiscal easing. This reflects the spillovers from stronger demand and trade in the advanced economies. Inflation would also rise due to the demand shock, but to a relatively limited extent.
Mitigating the impact of energy price increases on consumers
Lower-income countries and households spend the highest share of their incomes on energy and food (Figure 9). Governments had already introduced a range of measures to offset the effects of the large energy price increases seen before the start of the war. These measures are now being strengthened further. The policies used include income support, such as lump sum transfers, often means-tested. There have also been many price measures including lower electricity tariffs for low-income households, VAT cuts on electricity and gas, reductions in excise taxes on liquid fuels and electricity and energy price freezes. In some countries, subsidies have been provided to electricity companies to compensate for suppressing price increases.
To keep costs manageable, and avoid distorting price signals, additional support to offset the further energy price rises since the start of the war should be well targeted and temporary. Lower tax rates and price caps directly reduce the cost of energy, but benefit higher-income households as well as those most in need of help due to fuel poverty. Cash transfers can be better targeted, and have higher multiplier effects if focused on low-and-middle income households, but may take greater time to put in place and do not affect market prices.
Improving energy security by diversifying energy sources
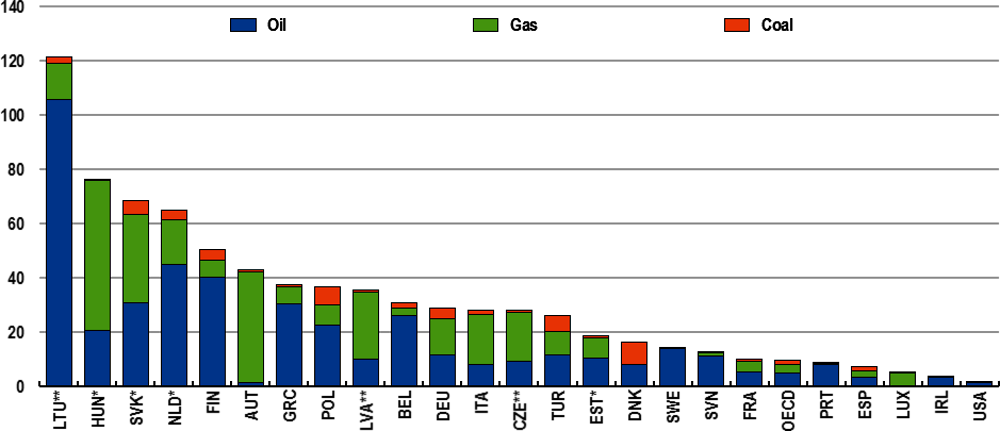
The war has starkly highlighted that many OECD economies are heavily reliant on fossil fuel energy with a high risk of price shocks and even shortages (Figure 10). Russia has provided over 40% of European natural gas imports until recently, a key source of heating for many EU households, a similar proportion of coal imports, and around one quarter of oil imports. Gas supply is also a major source of electricity production, with a key role in balancing demand and supply, and an input into industrial production such as fertilisers. Improving the security of energy supply in Europe is a medium-term venture, but significant gains can be achieved already in 2022. The IEA has set out a 10 Point Plan on how to reduce reliance on gas imports from Russia by between one-third and one-half over the next year.
In the longer term, OECD countries should reduce their overall reliance on fossil fuel imports by providing appropriate incentives to move away from fossil fuels and investing significantly in clean energy and energy efficiency. In Europe, improving the interconnection among domestic electricity grids can reduce energy costs and improve security. More generally, a strategic clean energy transition should aim to reduce vulnerabilities along the way, and be coupled with investment in innovation to develop the technologies needed for net-zero.
The main text incorporates simulations of the potential economic impact of the Russia-Ukraine conflict using the NiGEM global macroeconomic model. The simulations consider the impact of the shocks to commodity and financial markets seen in the first two weeks since the invasion by Russia, and large up-front declines in domestic demand in Russia and Ukraine.
The commodity price shocks are the percentage difference in the average price of selected commodities over February 24 to March 9 from the average price in January 2022. Translating these into the global commodity price aggregates included in NiGEM:
World oil prices are increased by 33% and coal prices by 80%.
Gas prices are raised by 85% in Europe, 10% in North America and 20% in the rest of the world.
World metals prices are increased by 11%, based on a weighted average of changes in prices for copper, gold, zinc, iron ore, nickel, aluminium, palladium and platinum.
World food prices are raised by a weighted average of 6%, with wheat prices up by 90%, corn prices by 40% and all other index components assumed to remain unchanged.
The financial market shocks are also calibrated on the average changes seen since the start of the war relative to January 2022. They include:
A 50% depreciation of the rouble against the US dollar, and an initial increase of 10.5 percentage points in Russian policy interest rates, with smaller bilateral US dollar currency depreciations of 5% in the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania and Turkey. These shocks imply small effective exchange rate appreciations in the major advanced economies.
Greater financial market uncertainty and diminished risk appetite has pushed up investment risk premia by around 1000 basis points in Russia, 500 basis points in Ukraine, 100 basis points in Turkey, 50 basis points in Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland and Romania, and 25 basis points in all other emerging-market economies.
The potential scale of the likely hit to domestic demand in Russia and Ukraine is extremely uncertain, but is likely to be large. Past episodes in Russia, such as the financial crisis in 1998 and the aftermath of the annexation of Crimea in 2014 were accompanied by sizeable domestic demand declines of between 10-15 per cent. The stronger sanctions applied following the invasion of Ukraine suggest that the downturn in Russia could be even larger than these past episodes. Sharp downturns have also occurred in other countries subject to international sanctions, including Iran. In Ukraine, the scale of the damage caused by the war is likely to be greater still. Other conflicts have resulted in annual GDP declines of between 25-40% in some countries, including Iraq, Syria and Yemen.
The simulations incorporate ex-ante domestic demand declines of 15% in Russia and 40% in Ukraine. Domestic demand is left endogenous to reflect other factors that are adjusting in the simulation.
All shocks are assumed to last for at least one year. The simulations are undertaken on the NiGEM model in backward-looking mode. This means that consumers and companies do not make their current spending choices with certainty about the future evolution of the conflict. Policy interest rates are endogenous and adjust according to the balance of the shocks to growth and inflation.
The fiscal scenario considers the impact of an increase in final government spending of 0.5% of GDP in all OECD economies. In practice, the measures taken could vary across countries, reflecting a combination of stronger investment and defence spending and cash transfers targeted on lower income households or refugees with a high marginal propensity to consume. In countries less directly affected by the conflict, the additional spending could also reflect temporary delays in some previously-planned discretionary consolidation.





אין תגובות:
הוסף רשומת תגובה